1. Reverse Linked List
Reverse Linked List - LeetCode
연결 리스트의 순서를 뒤집으면 되는 문제
next 포인터를 반대 방향으로 돌리면 된다.
-
코드
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val, next) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} head * @return {ListNode} */ var reverseList = function (head) { let [prev, curr] = [null, head]; while (curr) { next = curr.next; curr.next = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; };
2. Merge Two Sorted Lists
Merge Two Sorted Lists - LeetCode
두 정렬된 리스트를 하나로 합치는 문제
각 리스트의 노드를 하나씩 비교하며 작은 것을 앞에 붙이면 된다.
-
코드
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val, next) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} list1 * @param {ListNode} list2 * @return {ListNode} */ var mergeTwoLists = function (list1, list2) { let dummy = new ListNode(); let tail = dummy; while (list1 && list2) { if (list1.val <= list2.val) { tail.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; } else { tail.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; } tail = tail.next; } if (list1) { tail.next = list1; } if (list2) { tail.next = list2; } return dummy.next; };
3. Linked List Cycle
연결 리스트에 사이클이 존재하면 true, 존재하지 않으면 false를 반환하는 문제
사이클이 있는지 확인하기 위해 두 가지 방법을 사용할 수 있다.
-
Set을 이용하여 노드의 방문 여부를 확인하는 방법
-
플로이드의 토끼와 거북이 알고리즘(Floyd's Tortoise & Hare Algorithm)을 이용하는 방법
- 하나씩 움직이는 slow 포인터와 두개씩 움직이는 fast 포인터가 같은 위치에서 만나면 사이클 존재
-
코드 (Set을 이용한 방법)
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val) { * this.val = val; * this.next = null; * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} head * @return {boolean} */ var hasCycle = function (head) { let set = new Set(); while (head) { if (set.has(head)) { return true; } set.add(head); head = head.next; } return false; }; -
코드 (Floyd's Tortoise & Hare Algorithm)
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val) { * this.val = val; * this.next = null; * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} head * @return {boolean} */ var hasCycle = function (head) { let [s, f] = [head, head]; while (f && f.next) { s = s.next; f = f.next.next; if (s === f) { return true; } } return false; };
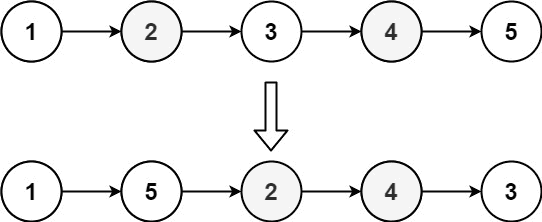
4. Reorder List
첫 번째 노드와 마지막 노드부터 번갈아가며 바꾸어 새로운 리스트를 만드는 문제
-
리스트를 절반으로 나눈다.
- slow, fast 포인터를 통해 반으로 나눌 수 있다.
- fast 포인터는 두개씩 움직이므로 fast 포인터가 끝에 도달했을 때 slow 포인터의 위치가 절반의 위치이다.
-
그리고 첫번째 리스트는 처음부터, 두번째 리스트는 끝에서부터 이어붙인다.
-
마지막 노드는 next를 null로 지정한다.
-
코드
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val, next) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} head * @return {void} Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead. */ var reorderList = function (head) { let [slow, fast] = [head, head.next]; while (fast && fast.next) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } // divide list let second = slow.next; slow.next = null; // reverse second list let prev = null; while (second) { let temp = second.next; second.next = prev; prev = second; second = temp; } // merge first & second list let first = head; second = prev; while (second) { let [temp1, temp2] = [first.next, second.next]; first.next = second; second.next = temp1; first = temp1; second = temp2; } };
5. Remove Nth Node From End of List
Remove Nth Node From End of List - LeetCode
끝에서 N번째 노드를 삭제하는 문제
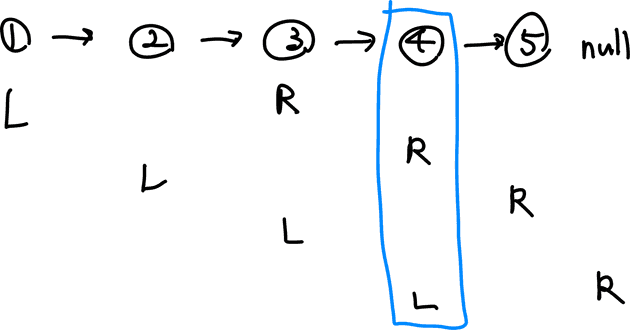
- 두 개의 포인터를 사용하는데 L 포인터와 R 포인터 사이의 간격이 N이 되도록 한다.
- R 포인터가 리스트의 끝(NULL)에 도달했을 때 L 포인터의 위치가 삭제할 노드의 위치가 된다.
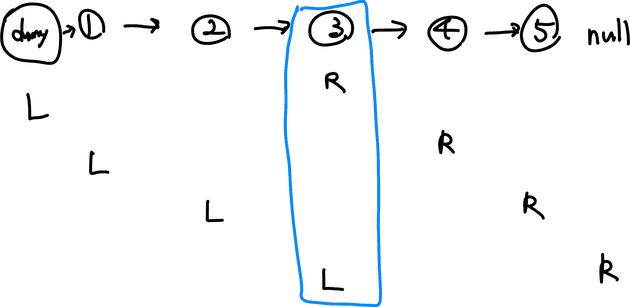
- 그러나 ‘4’ 노드를 삭제하기 위해서는 그 이전의 노드 ‘3’을 알고 있어야 하므로 편의상 리스트의 헤드 앞에 더미 노드를 붙여 L 포인터가 그 지점부터 시작할 수 있도록 한다. (R의 위치는 그대로 둔다.)
-
L 포인터가 ‘3’에 위치해 있는 상태에서 ‘5’에 연결하면 ‘4’가 삭제된다.
-
dummy.next를 반환한다.
-
코드
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val, next) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} head * @param {number} n * @return {ListNode} */ var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) { let dummy = new ListNode(); dummy.next = head; let [l, r] = [dummy, head]; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { r = r.next; } while (r) { l = l.next; r = r.next; } l.next = l.next.next; return dummy.next; };